- Welcome to Pulse Robot
- +86-23-63207381
- +8613677602178
- sales@pusirobot.com
Advantages and applications of stepper motors and drivers
Advantages and applications of stepper motors and drivers
A stepping motor is a motor that converts electrical pulse signals into corresponding angular displacements or linear displacements. Each time a pulse signal is input, the rotor rotates by an angle or one step forward. The output angular displacement or linear displacement is proportional to the number of input pulses, and the speed is proportional to the pulse frequency. Therefore, stepping motors are also called pulse motors.
Advantages of stepper motors:
- The angular displacement (or linear displacement) of a stepper motor is proportional to the number of electrical pulses, so the stepper motor (or linear speed) is also proportional to the pulse frequency. Within the load capacity of the stepper motor, its step angle and the speed is not affected by voltage fluctuations and load changes, and it is not affected by environmental conditions such as temperature, air pressure, impact and operation.) Pulse frequency. Therefore, the stepper motor is suitable as an actuator in an open loop system.
- The stepping motor has good control performance. By changing the pulse frequency, the speed (or linear speed) can be adjusted in a wide range, and it can quickly start, brake and reverse. If pulse electric motors with the same lead are used, they can run synchronously.
- The stepper motor has a fixed number of steps per revolution, and it runs without losing steps, and its step error will not accumulate. That is, although each step has an error, when it rotates once, the cumulative error is zero. These characteristics make it completely suitable for use as a servo component in a digitally controlled open-loop system, and make the whole system greatly simplified and reliable in operation. When the position detection device is adopted, it can also be used in a closed loop system.
- Some types of stepping motors still have positioning torque when the power supply is stopped, and some types of stepping motors still maintain the energized state of some phase windings after stopping. They also have self-locking ability and do not require mechanical braking devices.
- The step angle of a stepper motor has a large variation range. In the case of a small step angle, it is often possible to obtain low-speed operation without a reducer.
The stepper motor driver is an actuator that converts electrical pulses into angular displacement. When the stepper driver receives a pulse signal, it drives the stepper motor to rotate a fixed angle (called "step angle") in a set direction, and its rotation runs step by step at a fixed angle. The angular displacement can be controlled by controlling the number of pulses, so as to achieve the purpose of accurate positioning. At the same time, the speed and acceleration of the motor rotation can be controlled by controlling the pulse frequency, so as to achieve the purpose of speed regulation and positioning. The stepping motor and the stepping motor driver constitute a stepping motor drive system. The performance of the stepping motor drive system not only depends on the performance of the stepping motor itself, but also depends on the pros and cons of the stepping motor driver. The research on the stepper motor driver is carried out almost simultaneously with the research on the stepper motor.
Stepping motors cannot be directly connected to DC or AC power sources to work, and must use dedicated drivers. The driver (pulse signal generator) can control the angular displacement by controlling the number of pulses, so as to achieve the purpose of accurate positioning; at the same time, it can control the speed and acceleration of the motor rotation by controlling the pulse frequency, so as to achieve the purpose of speed regulation. As shown below.
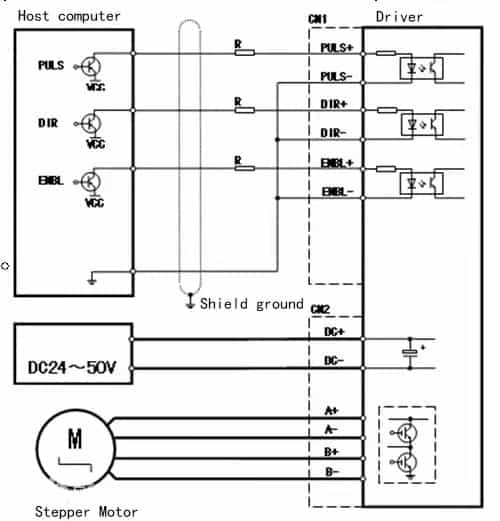
The conntecion of stepper motor and driver
Main features of PMD006xx:
- Support DC9-48V wide range single voltage power supply.
- The output current is continuously adjustable from 0.5-6A.
- The idle current is continuously adjustable from 0-100%.
- 0-128 subdivision, dial switch adjustment.
- Support 4/6/8 line two stepper motors.
- The input pulse frequency is up to 250KHz.
- With TSD, UVL0, OCP protection functions.
- Support full torque mode with enhanced torque.
- Support multiple input methods such as common anode, common cathode, differential, double pulse, pulse direction, etc.
- Stepper motor drivers are widely used in ATM machines, inkjet printers, plotters, photo machines, spraying equipment, medical instruments and equipment, computer peripherals and mass storage equipment, precision instruments, industrial control systems, office automation, robotics and other fields. It is especially suitable for applications requiring stable operation, low noise, fast response, long service life, and high output torque.
- Stepper motor drivers have a wide range of applications in textile machinery and equipment such as computer embroidery machines. The characteristics of this type of stepper motor are that the torque is not high, the frequent start-up response speed is fast, the running noise is low, the operation is stable, the control performance is good, and the Machine cost is low.

